August 27, 2024
P65 - Layout a binary tree (2).
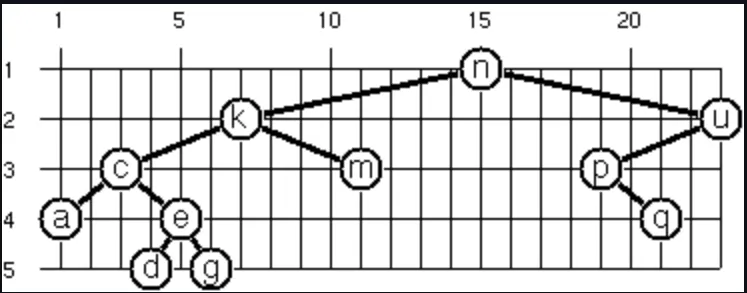
An alternative layout method is depicted in the illustration below (note that it is not the same tree as in the previous problem). This tree can be constructed with "nkmcaedgupq".toList().toTree().
Find out the rules and write the corresponding method.
Hint: On a given level, the horizontal distance between neighboring nodes is constant. Use the same conventions as in the problem P64.
> Node("a", Node("b", End, Node("c")), Node("d")).layout2()
T[3,1]('a T[1,2]('b . T[2,3]('c . .)) T[5,2]('d . .))kotlin
package org.kotlin99.binarytrees
import com.natpryce.hamkrest.assertion.assertThat
import com.natpryce.hamkrest.equalTo
import org.junit.Test
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.P64Test.Companion.toPrettyString
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.Tree.End
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.Tree.Node
import kotlin.math.pow
fun <T> Tree<T>.layout2(
x: Int = leftmostBranchXShift(),
y: Int = 1,
spaces: Spaces = Spaces(this)
): Tree<Positioned<T>> =
when (this) {
End -> End
is Node<T> -> Node(
value = Positioned(value, x, y),
left = left.layout2(x - spaces.toInt(), y + 1, spaces.decrease()),
right = right.layout2(x + spaces.toInt(), y + 1, spaces.decrease())
)
}
data class Spaces(val value: Int) {
constructor(tree: Tree<*>): this(tree.height() - 2)
fun decrease() = Spaces(value - 1)
fun toInt() = 2.pow(value)
}
private fun Tree<*>.leftmostBranchXShift(): Int {
fun leftmostBranchHeight(tree: Tree<*>): Int {
return when (tree) {
End -> 0
is Node -> leftmostBranchHeight(tree.left) + 1
}
}
val height = height() // Need the whole tree height here because leftmost branch might not be the tallest branch.
return (2..leftmostBranchHeight(this)).sumOf { Spaces(height - it).toInt() } + 1
}
private fun Int.pow(n: Int): Int = this.toDouble().pow(n.toDouble()).toInt()
class P65Test {
@Test fun `layout binary tree (2)`() {
assertThat(
Node("a").layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012
|0···
|1·a·
|2···
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b")).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 0123
|0····
|1··a·
|2·b··
|3····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("c"))).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345
|0······
|1····a·
|2··b···
|3·c····
|4······
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("c", Node("d")))).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 0123456789
|0··········
|1········a·
|2····b·····
|3··c·······
|4·d········
|5··········
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", End, Node("b", End, Node("c"))).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345
|0······
|1·a····
|2···b··
|3····c·
|4······
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b"), Node("c")).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 01234
|0·····
|1··a··
|2·b·c·
|3·····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("d"), Node("e")), Node("c", Node("f"), Node("g"))).layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345678
|0·········
|1····a····
|2··b···c··
|3·d·e·f·g·
|4·········
""".trimMargin()))
}
@Test fun `illustration example`() {
assertThat(
"nkmcaedgupq".toList().toTree().layout2().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 0123456789012345678901234
|0·························
|1···············n·········
|2·······k···············u·
|3···c·······m·······p·····
|4·a···e···············q···
|5····d·g··················
|6·························
""".trimMargin()))
}
}