August 27, 2024
P66 - Layout a binary tree (3).
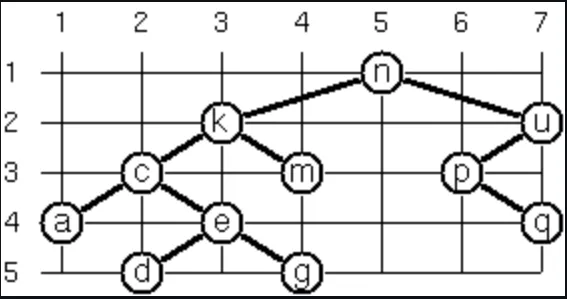
Yet another layout strategy is shown in the illustration below. This tree can be constructed with "nkmcaedgupq".toList().toTree().
The method yields a very compact layout while maintaining a certain symmetry in every node. Find out the rules and write the corresponding method. Hint: Consider the horizontal distance between a node and its successor nodes.
How tight can you pack together two subtrees to construct the combined binary tree? Use the same conventions as in problem P64 and P65. Note: This is a difficult problem. Don't give up too early!
> Node('a', Node('b', End, Node('c')), Node('d')).layoutBinaryTree3()
T[2,1]('a T[1,2]('b . T[2,3]('c . .)) T[3,2]('d . .))Which layout do you like most?
kotlin
package org.kotlin99.binarytrees
import com.natpryce.hamkrest.assertion.assertThat
import com.natpryce.hamkrest.equalTo
import org.junit.Test
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.P64Test.Companion.toPrettyString
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.Tree.End
import org.kotlin99.binarytrees.Tree.Node
fun <T> Tree<T>.layout3(parentX: Int? = null, shiftFromParent: Int = 0, y: Int = 1): Tree<Positioned<T>> {
return when (this) {
End -> End
is Node<T> -> {
fun haveNoPositionOverlap(tree1: Tree<Positioned<*>>, tree2: Tree<Positioned<*>>): Boolean =
(tree1.nodes().map { it.value.point }.intersect(tree2.nodes().map { it.value.point })).isEmpty()
var shift = 1
while (shift < 100) {
var x = parentX?.plus(shiftFromParent)
val positionedLeft = left.layout3(x, -shift, y + 1)
if (parentX == null && positionedLeft is Node<Positioned<T>>) {
x = positionedLeft.value.point.x + shift
} else if (parentX == null) {
x = 1
}
val positionedRight = right.layout3(x, shift, y + 1)
if (haveNoPositionOverlap(positionedLeft, positionedRight)) {
return Node(Positioned(value, x!!, y), positionedLeft, positionedRight)
}
shift += 1
}
throw IllegalStateException()
}
}
}
class P66Test {
@Test fun `layout binary tree (3)`() {
assertThat(
Node("a").layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012
|0···
|1·a·
|2···
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b")).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 0123
|0····
|1··a·
|2·b··
|3····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("c"))).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 01234
|0·····
|1···a·
|2··b··
|3·c···
|4·····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("c", Node("d")))).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345
|0······
|1····a·
|2···b··
|3··c···
|4·d····
|5······
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", End, Node("b", End, Node("c"))).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 01234
|0·····
|1·a···
|2··b··
|3···c·
|4·····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", End, Node("d")), Node("c")).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 01234
|0·····
|1··a··
|2·b·c·
|3··d··
|4·····
""".trimMargin()))
assertThat(
Node("a", Node("b", Node("d"), Node("e")), Node("c", Node("f"), Node("g"))).layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345678
|0·········
|1····a····
|2··b···c··
|3·d·e·f·g·
|4·········
""".trimMargin()))
}
@Test fun `illustration example`() {
assertThat(
"nkmcaedgupq".toList().toTree().layout3().toPrettyString(),
equalTo("""
| 012345678
|0·········
|1·····n···
|2···k···u·
|3··c·m·p··
|4·a·e···q·
|5··d·g····
|6·········
""".trimMargin()))
}
}