August 21, 2024
P73 - Prolog-like tree representation
There is a particular notation for multiway trees in Prolog. Prolog is a prominent functional programming language, which is used primarily for artificial intelligence problems. As such, it is one of the main competitors of Lisp. In Prolog everything is a term, just as in Lisp everything is a symbolic expression.
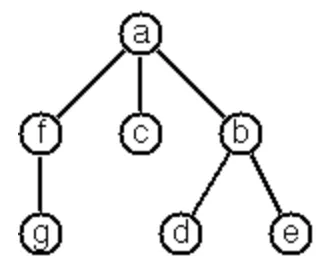
In Prolog we represent a multiway tree by a term t(X,F), where X denotes the root node and F denotes the forest of successor trees (a Prolog list). The example tree depicted opposite is represented by the following Lisp expression:
t(a,[t(f,[t(g,[])]),t(c,[]),t(b,[t(d,[]),t(e,[])])])
The Prolog representation of a multiway tree is a sequence of atoms, commas, parentheses "(" and ")", and brackets "[" and "]".which we shall collectively call "tokens". We can represent this sequence of tokens as a Lisp list; e.g. the Prolog expression t(a,[t(b,[]),t(c,[])]) could be represented as the Lisp list ( t "(" a "," "[" t "(" b "," "[" "]" ")" "," t "(" c "," "[" "]" ")" "]" ")" ). Write a function (tree-ptl expr) which returns the "Prolog token list" if the tree is given as an expression expr in the usual Lisp notation.Example:* (tree-ptl '(a b c))( T "(" A "," "[" T "(" B "," "[" "]" ")" "," T "(" C "," "[" "]" ")" "]" ")" )
As a second, even more interesting exercise try to write the inverse conversion: Given the list PTL, construct the corresponding Lisp tree.
lisp
(defun tree-ptl (tree)
(cond
((null tree) ())
((atom tree) (list t "(" tree "," "[" "]" ")"))
(t (append (list t "(" (first tree) "," "[")
(ptl-list (children tree))
(list "]" ")")
)
)
)
)
(defun children (tree)
(rest tree)
)
(defun ptl-list (children)
(cond
((null children) ())
((null (rest children)) (tree-ptl (first children)))
(t (append (tree-ptl (first children))
(list ",")
(ptl-list (rest children))
))
)
)