August 27, 2024
P64 - Layout a binary tree (1).
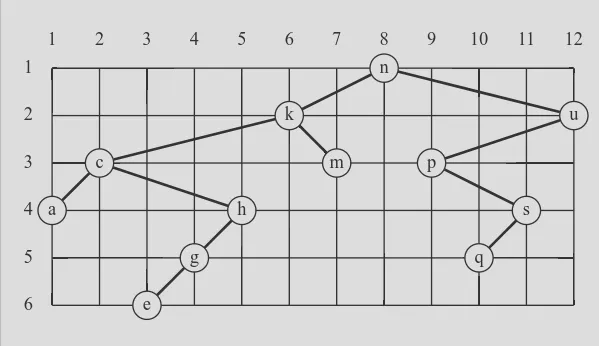
As a preparation for drawing a tree, a layout algorithm is required to determine the position of each node in a rectangular grid. Several layout methods are conceivable, one of them is shown in the illustration on the right.
In this layout strategy, the position of a node vv is obtained by the following two rules:
- xvxv is equal to the position of the node vv in the inorder sequence
- yvyv is equal to the depth of the node vv in the tree
In order to store the position of the nodes, we add a new class with the additional information.
scala
case class PositionedNode[+T](override val value: T, override val left: Tree[T], override val right: Tree[T], x: Int, y: Int) extends Node[T](value, left, right) {
override def toString = "T[" + x.toString + "," + y.toString + "](" + value.toString + " " + left.toString + " " + right.toString + ")"
}
Write a method layoutBinaryTree that turns a tree of normal Nodes into a tree of PositionedNodes.
scala
scala> Node('a', Node('b', End, Node('c')), Node('d')).layoutBinaryTree
res0: PositionedNode[Char] = T[3,1](a T[1,2](b . T[2,3](c . .)) T[4,2](d . .))
The tree at right may be constructed with Tree.fromList(List('n', 'k', 'm', 'c', 'a', 'h', 'g', 'e', 'u', 'p', 's', 'q')). Use it to check your code.